Bạn có biết rằng 80% logic xử lý của một ứng dụng web diễn ra ở backend mà người dùng không bao giờ nhìn thấy? Trong thời đại công nghệ số phát triển mạnh mẽ, backend development đã trở thành xương sống của mọi hệ thống số từ hệ thống website đơn giản đến các platform phức tạp như Facebook, Netflix hay Shopee. Khác với frontend chỉ tập trung vào giao diện, backend chính là “bộ não” điều khiển toàn bộ hoạt động của ứng dụng – từ xử lý dữ liệu, bảo mật, đến tích hợp các dịch vụ bên thứ ba. Tuy nhiên, nhiều người vẫn chưa hiểu rõ backend developer làm gì, cần những kỹ năng nào và tại sao mức lương backend thường cao hơn frontend. Bài viết này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu sâu về thế giới backend development, các công nghệ cốt lõi, kiến trúc hệ thống và lộ trình trở thành backend developer chuyên nghiệp. Đặc biệt, chúng tôi sẽ chia sẻ những xu hướng mới nhất và cơ hội nghề nghiệp trong lĩnh vực backend năm 2025.
Backend Là Gì? Định Nghĩa Chi Tiết Về Lập Trình Phía Server
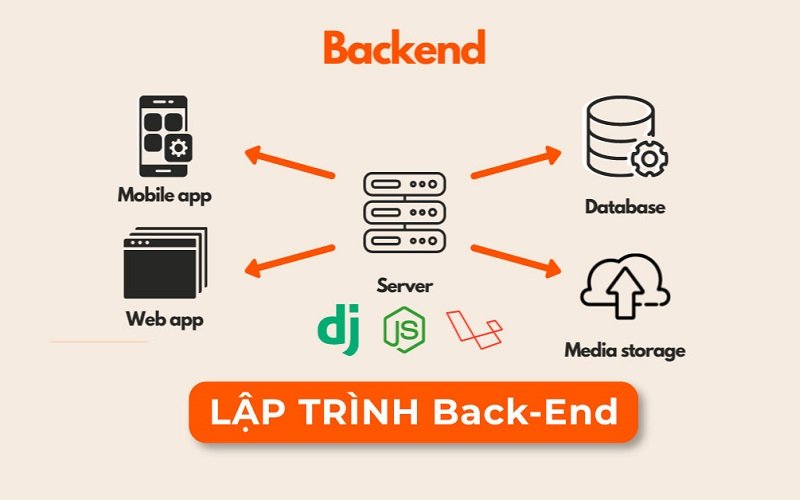
Backend (hay Back-end) là phần xử lý logic phía server của một ứng dụng, bao gồm tất cả những gì diễn ra “phía sau hậu trường” mà người dùng cuối không nhìn thấy. Nếu frontend là “mặt tiền” của một cửa hàng, thì backend chính là “kho hàng, hệ thống quản lý và nhân viên” làm việc bên trong.
Vai Trò Của Backend Trong Hệ Thống
Backend đảm nhận những chức năng cốt lõi sau:
Xử lý Logic Nghiệp Vụ:
- Business Logic: Các quy tắc và quy trình nghiệp vụ
- Data Processing: Xử lý, tính toán và biến đổi dữ liệu
- Workflow Management: Quản lý luồng công việc
- Integration: Tích hợp với các hệ thống bên thứ ba
Quản Lý Dữ Liệu:
- Database Operations: CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete)
- Data Validation: Kiểm tra tính hợp lệ của dữ liệu
- Data Security: Mã hóa và bảo vệ dữ liệu nhạy cảm
- Backup & Recovery: Sao lưu và khôi phục dữ liệu
Bảo Mật Hệ Thống:
- Authentication: Xác thực người dùng
- Authorization: Phân quyền truy cập
- Security Monitoring: Giám sát bảo mật
- Vulnerability Management: Quản lý lỗ hổng bảo mật
Sự Khác Biệt Giữa Backend Và Frontend
| Tiêu chí | Backend | Frontend |
|---|---|---|
| Vị trí | Server-side | Client-side |
| Người dùng | Không nhìn thấy | Tương tác trực tiếp |
| Ngôn ngữ | Java, Python, C#, Node.js | HTML, CSS, JavaScript |
| Trách nhiệm | Logic, database, API | Giao diện, UX |
| Performance | Tối ưu server | Tối ưu browser |
| Bảo mật | Bảo mật toàn hệ thống | Bảo mật client |
Backend Trong Kiến Trúc Ứng Dụng Hiện Đại
Kiến trúc 3-tier truyền thống:
Presentation Layer (Frontend) → Business Logic Layer (Backend) → Data Layer (Database)Kiến trúc Microservices hiện đại:
Frontend → API Gateway → Service A, B, C → Databases, Cache, Message QueueVai trò trong Cloud Architecture:
- Containerization: Docker, Kubernetes
- Serverless: AWS Lambda, Azure Functions
- Cloud Services: Cơ sở dữ liệu Database, Storage, Monitoring
- DevOps Integration: CI/CD, Infrastructure as Code
Ngôn Ngữ Lập Trình Backend Phổ Biến Nhất

Java – Ngôn Ngữ Enterprise Hàng Đầu
Java là ngôn ngữ lập trình backend phổ biến nhất trong các doanh nghiệp lớn.
Ưu điểm của Java:
- Platform Independent: “Write once, run anywhere”
- Strong Typing: Kiểm tra lỗi tại compile time
- Rich Ecosystem: Spring Framework, Hibernate
- Enterprise Features: JEE, microservices support
- Performance: JVM optimization, garbage collection
Frameworks Java phổ biến:
- Spring Boot: Rapid application development
- Spring Security: Authentication & authorization
- Hibernate: Object-Relational Mapping (ORM)
- Apache Kafka: Message streaming platform
Ví dụ Spring Boot REST API:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
User user = userService.findById(id);
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<User> createUser(@RequestBody @Valid User user) {
User savedUser = userService.save(user);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(savedUser);
}
}Python – Ngôn Ngữ Đa Năng Và Dễ Học
Python nổi tiếng với syntax đơn giản và ecosystem phong phú.
Ưu điểm của Python:
- Readable Code: Syntax gần với ngôn ngữ tự nhiên
- Rapid Development: Phát triển nhanh với ít code
- Rich Libraries: NumPy, Pandas, TensorFlow
- AI/ML Integration: Machine Learning, Data Science
- Community Support: Cộng đồng lớn và tích cực
Frameworks Python phổ biến:
- Django: Full-featured web framework
- FastAPI: Modern, fast API framework
- Flask: Lightweight, flexible framework
- Celery: Distributed task queue
Ví dụ FastAPI:
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import List
app = FastAPI()
class User(BaseModel):
id: int
name: str
email: str
users_db = []
@app.get("/users", response_model=List[User])
async def get_users():
return users_db
@app.post("/users", response_model=User)
async def create_user(user: User):
users_db.append(user)
return user
@app.get("/users/{user_id}", response_model=User)
async def get_user(user_id: int):
user = next((u for u in users_db if u.id == user_id), None)
if not user:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="User not found")
return userNode.js – JavaScript Phía Server
Node.js cho phép sử dụng JavaScript để phát triển backend.
Ưu điểm của Node.js:
- Single Language: JavaScript cho cả frontend và backend
- Event-Driven: Non-blocking I/O operations
- NPM Ecosystem: Hàng triệu packages
- Real-time Applications: WebSocket, chat apps
- Microservices Friendly: Lightweight, scalable
Frameworks Node.js phổ biến:
- Express.js: Minimal web framework
- NestJS: Enterprise-grade framework
- Koa.js: Next-generation web framework
- Socket.io: Real-time communication
C# (.NET) – Giải Pháp Microsoft
C# với .NET framework là lựa chọn mạnh mẽ cho enterprise applications.
Ưu điểm của C#:
- Type Safety: Strong typing system
- Performance: Compiled language
- Integration: Tích hợp tốt với Microsoft ecosystem
- Cross-platform: .NET Core/5+ chạy trên Linux, macOS
- Enterprise Features: Security, scalability
So Sánh Ngôn Ngữ Backend
| Ngôn ngữ | Performance | Learning Curve | Ecosystem | Enterprise |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Java | Cao | Trung bình | Rất phong phú | Tuyệt vời |
| Python | Trung bình | Dễ | Phong phú | Tốt |
| Node.js | Cao | Dễ | Rất phong phú | Tốt |
| C# | Cao | Trung bình | Phong phú | Tuyệt vời |
| Go | Rất cao | Trung bình | Đang phát triển | Tốt |
| Rust | Rất cao | Khó | Đang phát triển | Trung bình |
Database Và Quản Lý Dữ Liệu Backend
Relational Databases (SQL)
MySQL:
- Ưu điểm: Miễn phí, reliable, community support
- Sử dụng: Web applications, e-commerce
- Performance: Tốt cho read-heavy workloads
- Scaling: Master-slave replication
PostgreSQL:
- Ưu điểm: Advanced features, ACID compliance
- Sử dụng: Complex applications, analytics
- Performance: Tốt cho write-heavy workloads
- Features: JSON support, full-text search
Ví dụ SQL query tối ưu:
-- Index optimization
CREATE INDEX idx_user_email ON users(email);
CREATE INDEX idx_order_date ON orders(created_at);
-- Complex query with joins
SELECT
u.name,
u.email,
COUNT(o.id) as total_orders,
SUM(o.amount) as total_spent
FROM users u
LEFT JOIN orders o ON u.id = o.user_id
WHERE u.created_at >= '2024-01-01'
GROUP BY u.id, u.name, u.email
HAVING COUNT(o.id) > 0
ORDER BY total_spent DESC
LIMIT 100;NoSQL Databases
MongoDB:
- Document-based: JSON-like documents
- Flexible Schema: Dynamic data structure
- Horizontal Scaling: Sharding support
- Use Cases: Content management, IoT, real-time analytics
Redis:
- In-memory: Extremely fast access
- Data Structures: Strings, lists, sets, hashes
- Use Cases: Caching, session storage, pub/sub
- Performance: Sub-millisecond latency
Ví dụ MongoDB operations:
// Insert document
await db.collection('users').insertOne({
name: 'John Doe',
email: 'john@example.com',
profile: {
age: 30,
city: 'Ho Chi Minh City'
},
tags: ['developer', 'nodejs']
});
// Complex aggregation
const result = await db.collection('orders').aggregate([
{ $match: { status: 'completed' } },
{ $group: {
_id: '$userId',
totalOrders: { $sum: 1 },
totalAmount: { $sum: '$amount' }
}},
{ $sort: { totalAmount: -1 } },
{ $limit: 10 }
]);Database Design Best Practices
Normalization vs Denormalization:
- 3NF: Eliminate data redundancy
- Denormalization: Optimize for read performance
- Trade-offs: Storage vs query performance
Indexing Strategies:
- Primary Index: Unique identifier
- Secondary Index: Query optimization
- Composite Index: Multiple columns
- Partial Index: Conditional indexing
Caching Layers:
- Application Cache: In-memory caching
- Database Cache: Query result caching
- CDN: Static content caching
- Redis/Memcached: Distributed caching
API Development Và RESTful Services
REST API Design Principles
REST (Representational State Transfer) là architectural style phổ biến nhất cho web APIs.
6 Nguyên tắc REST:
- Client-Server: Tách biệt client và server
- Stateless: Mỗi request độc lập
- Cacheable: Response có thể cache
- Uniform Interface: Interface nhất quán
- Layered System: Kiến trúc nhiều lớp
- Code on Demand: Optional client-side code
HTTP Methods và Usage:
GET /api/users # Lấy danh sách users
GET /api/users/123 # Lấy user cụ thể
POST /api/users # Tạo user mới
PUT /api/users/123 # Cập nhật toàn bộ user
PATCH /api/users/123 # Cập nhật một phần user
DELETE /api/users/123 # Xóa userAPI Documentation Và Testing
OpenAPI/Swagger:
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: User Management API
version: 1.0.0
paths:
/users:
get:
summary: Get all users
responses:
'200':
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: array
items:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/User'
components:
schemas:
User:
type: object
properties:
id:
type: integer
name:
type: string
email:
type: stringAPI Testing Tools:
- Postman: Interactive API testing
- Insomnia: REST client
- curl: Command-line testing
- Jest/Mocha: Automated testing
GraphQL – Alternative To REST
GraphQL cho phép client request chính xác data cần thiết.
Ưu điểm GraphQL:
- Single Endpoint: Một endpoint cho tất cả
- Flexible Queries: Client định nghĩa data structure
- Type System: Strong typing
- Real-time: Subscriptions support
Ví dụ GraphQL schema:
type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
email: String!
posts: [Post!]!
}
type Post {
id: ID!
title: String!
content: String!
author: User!
}
type Query {
users: [User!]!
user(id: ID!): User
posts: [Post!]!
}
type Mutation {
createUser(input: CreateUserInput!): User!
updateUser(id: ID!, input: UpdateUserInput!): User!
deleteUser(id: ID!): Boolean!
}Kiến Trúc Backend Và System Design
Monolithic vs Microservices
Monolithic Architecture:
- Đặc điểm: Single deployable unit
- Ưu điểm: Đơn giản, dễ develop và test
- Nhược điểm: Khó scale, technology lock-in
- Phù hợp: Small teams, simple applications
Microservices Architecture:
- Đặc điểm: Multiple independent services
- Ưu điểm: Scalable, technology diversity
- Nhược điểm: Complex, network overhead
- Phù hợp: Large teams, complex domains
Load Balancing Và Scaling
Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling:
- Vertical Scaling: Tăng cấu hình server
- Horizontal Scaling: Thêm nhiều server
- Auto Scaling: Tự động scale theo load
Load Balancer Types:
- Layer 4: Transport layer (TCP/UDP)
- Layer 7: Application layer (HTTP/HTTPS)
- Algorithms: Round-robin, least connections, weighted
Caching Strategies:
Cache-Aside Pattern:
1. Check cache first
2. If miss, query database
3. Update cache with result
Write-Through Pattern:
1. Write to cache
2. Cache writes to database
3. Confirm write completion
Write-Behind Pattern:
1. Write to cache immediately
2. Asynchronously write to database
3. Better write performanceMessage Queues Và Event-Driven Architecture
Message Queue Benefits:
- Decoupling: Services không phụ thuộc trực tiếp
- Reliability: Message persistence
- Scalability: Handle traffic spikes
- Fault Tolerance: Retry mechanisms
Popular Message Brokers:
- RabbitMQ: Feature-rich, reliable
- Apache Kafka: High-throughput streaming
- Redis Pub/Sub: Simple publish-subscribe
- Amazon SQS: Managed queue service
Event-Driven Architecture Example:
// Producer
const publishEvent = async (eventType, data) => {
const event = {
id: generateUUID(),
type: eventType,
timestamp: new Date(),
data: data
};
await messageQueue.publish('events', event);
};
// Consumer
messageQueue.subscribe('events', async (event) => {
switch(event.type) {
case 'USER_CREATED':
await sendWelcomeEmail(event.data);
break;
case 'ORDER_PLACED':
await processPayment(event.data);
break;
}
});Bảo Mật Backend Và Best Practices
Authentication Và Authorization
JWT (JSON Web Tokens):
// Generate JWT
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const generateToken = (user) => {
return jwt.sign(
{
userId: user.id,
email: user.email,
role: user.role
},
process.env.JWT_SECRET,
{ expiresIn: '24h' }
);
};
// Verify JWT Middleware
const authenticateToken = (req, res, next) => {
const authHeader = req.headers['authorization'];
const token = authHeader && authHeader.split(' ')[1];
if (!token) {
return res.sendStatus(401);
}
jwt.verify(token, process.env.JWT_SECRET, (err, user) => {
if (err) return res.sendStatus(403);
req.user = user;
next();
});
};OAuth 2.0 Flow:
- Authorization Request: Client request authorization
- Authorization Grant: User grants permission
- Access Token Request: Exchange grant for token
- Access Token Response: Server returns token
- Protected Resource: Access with token
Input Validation Và SQL Injection Prevention
Input Validation:
const { body, validationResult } = require('express-validator');
const validateUser = [
body('email').isEmail().normalizeEmail(),
body('password').isLength({ min: 8 }).matches(/^(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*\d)/),
body('name').trim().isLength({ min: 2, max: 50 }),
(req, res, next) => {
const errors = validationResult(req);
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
return res.status(400).json({ errors: errors.array() });
}
next();
}
];SQL Injection Prevention:
// BAD - Vulnerable to SQL injection
const query = `SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = '${email}'`;
// GOOD - Using parameterized queries
const query = 'SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = ?';
db.query(query, [email], (err, results) => {
// Handle results
});
// GOOD - Using ORM
const user = await User.findOne({ where: { email: email } });HTTPS Và Data Encryption
TLS/SSL Configuration:
const https = require('https');
const fs = require('fs');
const options = {
key: fs.readFileSync('private-key.pem'),
cert: fs.readFileSync('certificate.pem')
};
https.createServer(options, app).listen(443, () => {
console.log('HTTPS Server running on port 443');
});Data Encryption:
const bcrypt = require('bcrypt');
const crypto = require('crypto');
// Password hashing
const hashPassword = async (password) => {
const saltRounds = 12;
return await bcrypt.hash(password, saltRounds);
};
// Sensitive data encryption
const encrypt = (text) => {
const algorithm = 'aes-256-gcm';
const key = Buffer.from(process.env.ENCRYPTION_KEY, 'hex');
const iv = crypto.randomBytes(16);
const cipher = crypto.createCipher(algorithm, key);
cipher.setAAD(Buffer.from('additional-data'));
let encrypted = cipher.update(text, 'utf8', 'hex');
encrypted += cipher.final('hex');
const authTag = cipher.getAuthTag();
return {
encrypted,
iv: iv.toString('hex'),
authTag: authTag.toString('hex')
};
};Lộ Trình Học Backend Development Chi Tiết
Giai Đoạn 1: Nền Tảng Cơ Bản (3-4 tháng)
Kiến thức cơ sở:
- Programming Fundamentals: Variables, functions, OOP
- Data Structures: Arrays, lists, maps, trees
- Algorithms: Sorting, searching, complexity
- Database Basics: SQL, relational concepts
Chọn ngôn ngữ chính:
- Python: Dễ học, syntax đơn giản
- Java: Enterprise-ready, strong typing
- Node.js: JavaScript ecosystem
- C#: Microsoft stack
Dự án thực hành:
- CRUD application với database
- Simple REST API
- User authentication system
- File upload/download service
Giai Đoạn 2: Web Development Fundamentals (2-3 tháng)
HTTP Protocol:
- Request/Response cycle
- HTTP methods và status codes
- Headers và cookies
- Session management
API Development:
- RESTful API design
- JSON data format
- API documentation
- Error handling
Database Operations:
- Advanced SQL queries
- Database design principles
- Indexing và optimization
- Transactions và ACID
Dự án thực hành:
- E-commerce API
- Blog management system
- User management with roles
- File storage service
Giai Đoạn 3: Advanced Backend Concepts (4-5 tháng)
System Architecture:
- Microservices patterns
- Load balancing
- Caching strategies
- Message queues
Security:
- Authentication/Authorization
- JWT tokens
- OAuth 2.0
- Data encryption
Performance:
- Database optimization
- Caching layers
- Code profiling
- Monitoring tools
Dự án thực hành:
- Microservices application
- Real-time chat system
- Payment processing system
- Analytics dashboard
Giai Đoạn 4: Production Ready Skills (3-6 tháng)
DevOps Integration:
- Docker containerization
- CI/CD pipelines
- Cloud deployment (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Infrastructure as Code
Monitoring & Logging:
- Application monitoring
- Log aggregation
- Error tracking
- Performance metrics
Advanced Topics:
- Event-driven architecture
- CQRS và Event Sourcing
- Distributed systems
- Scalability patterns
Soft Skills:
- Code review practices
- Technical documentation
- Team collaboration
- Problem-solving
Cơ Hội Nghề Nghiệp Và Mức Lương Backend Developer
Các Vị Trí Backend Developer
Junior Backend Developer:
- Mức lương: 10-18 triệu VNĐ/tháng
- Kinh nghiệm: 0-2 năm
- Yêu cầu: Một ngôn ngữ backend, SQL cơ bản, REST API
Mid-level Backend Developer:
- Mức lương: 18-30 triệu VNĐ/tháng
- Kinh nghiệm: 2-4 năm
- Yêu cầu: Framework, database design, system architecture
Senior Backend Developer:
- Mức lương: 30-50 triệu VNĐ/tháng
- Kinh nghiệm: 4+ năm
- Yêu cầu: System design, mentoring, performance optimization
Backend Architect:
- Mức lương: 50-80 triệu VNĐ/tháng
- Kinh nghiệm: 6+ năm
- Yêu cầu: Distributed systems, technical leadership
DevOps Engineer:
- Mức lương: 25-45 triệu VNĐ/tháng
- Yêu cầu: Backend + infrastructure, CI/CD, cloud platforms
Xu Hướng Tuyển Dụng Backend 2025
Công nghệ được ưa chuộng:
- Cloud Native: 65% job postings
- Microservices: 55% yêu cầu
- Container Technology: Docker 70%, Kubernetes 40%
- Message Queues: Kafka 30%, RabbitMQ 25%
- NoSQL: MongoDB 45%, Redis 60%
Ngành nghề tuyển dụng nhiều:
- Fintech: Banking, payments, cryptocurrency
- E-commerce: Marketplace, logistics
- Gaming: Online games, platforms
- Healthcare: Telemedicine, health records
- IoT: Smart devices, data processing
Remote Work Và Freelance
Remote Opportunities:
- 85% backend jobs hỗ trợ remote work
- International clients với mức lương USD
- Flexible working arrangements
- Global collaboration experience
Freelance Projects:
- API Development: 20-100 triệu VNĐ
- Database Design: 15-50 triệu VNĐ
- System Integration: 50-200 triệu VNĐ
- Performance Optimization: 30-150 triệu VNĐ
Xu Hướng Backend Development Năm 2025
Serverless Architecture
Function as a Service (FaaS):
- AWS Lambda: Event-driven computing
- Azure Functions: Serverless compute
- Google Cloud Functions: HTTP triggers
- Vercel Functions: Edge computing
Benefits:
- Cost Effective: Pay per execution
- Auto Scaling: Handle traffic spikes
- No Server Management: Focus on code
- Fast Deployment: Quick iterations
Cloud-Native Development
Container Orchestration:
- Kubernetes: Container orchestration platform
- Docker Swarm: Simple container clustering
- Service Mesh: Istio, Linkerd for microservices
- Serverless Containers: AWS Fargate, Google Cloud Run
Cloud Services Integration:
- Database as a Service: RDS, CosmosDB
- Message Queues: SQS, Service Bus
- Storage: S3, Blob Storage
- Monitoring: CloudWatch, Application Insights
AI/ML Integration
Machine Learning APIs:
- Prediction Services: TensorFlow Serving
- Natural Language Processing: OpenAI GPT, Google NLP
- Computer Vision: AWS Rekognition, Azure Cognitive Services
- Recommendation Engines: Collaborative filtering
MLOps Practices:
- Model Versioning: MLflow, DVC
- Automated Training: Kubeflow, Azure ML
- A/B Testing: Feature flags, gradual rollout
- Monitoring: Model drift detection
Event-Driven Architecture Evolution
Event Streaming Platforms:
- Apache Kafka: High-throughput streaming
- Apache Pulsar: Multi-tenant messaging
- AWS Kinesis: Real-time data streams
- Azure Event Hubs: Big data streaming
Event Sourcing Patterns:
- Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS)
- Event Store: Immutable event log
- Saga Pattern: Distributed transactions
- Event-driven Microservices
Câu Hỏi Thường Gặp Về Backend Development
Backend developer cần học những gì đầu tiên?
Bắt đầu với một ngôn ngữ lập trình (Python/Java/Node.js), học SQL và database cơ bản, sau đó tìm hiểu về HTTP protocol và REST API development.
Mất bao lâu để trở thành backend developer?
Với việc học 3-4 giờ/ngày, bạn có thể có kiến thức cơ bản trong 8-10 tháng và sẵn sàng cho vị trí junior trong 10-15 tháng. Tuy nhiên, để thành thạo cần 2-3 năm kinh nghiệm thực tế.
Backend có khó học hơn frontend không?
Backend có learning curve dốc hơn vì cần hiểu về database, server architecture, và security. Tuy nhiên, backend ít thay đổi hơn frontend nên kiến thức bền vững hơn.
Nên chọn ngôn ngữ nào để học backend?
Python phù hợp người mới bắt đầu, Java tốt cho enterprise, Node.js nếu đã biết JavaScript, C# cho Microsoft ecosystem. Quan trọng là nắm vững một ngôn ngữ trước khi học thêm.
Backend developer có cần biết frontend không?
Không bắt buộc nhưng hiểu cơ bản về frontend sẽ giúp thiết kế API tốt hơn và giao tiếp hiệu quả với frontend team. Fullstack developer có lợi thế về mức lương.
Làm sao để cập nhật kiến thức backend liên tục?
Theo dõi tech blogs (High Scalability, Martin Fowler), tham gia conferences, đọc documentation của cloud providers, practice với side projects và contribute vào open source.
Kết Luận: Con Đường Trở Thành Backend Developer Chuyên Nghiệp
Backend development là trái tim của mọi ứng dụng hiện đại, nơi mà logic nghiệp vụ, bảo mật và hiệu suất được quyết định. Trong thời đại mà dữ liệu là tài sản quý giá nhất và bảo mật là ưu tiên hàng đầu, vai trò của backend developer trở nên quan trọng hơn bao giờ hết.
Những điểm quan trọng cần ghi nhớ:
- Backend là nền tảng vững chắc cho mọi ứng dụng thành công
- Nắm vững một ngôn ngữ lập trình và database trước khi mở rộng
- System design và architecture thinking là kỹ năng phân biệt senior
- Security và performance optimization là yêu cầu không thể thiếu
- Cloud computing và DevOps là xu hướng không thể bỏ qua
Roadmap thành công cho backend developer:
- Xây dựng nền tảng vững chắc với programming fundamentals
- Thành thạo một tech stack (ngôn ngữ + framework + database)
- Hiểu sâu về system architecture và design patterns
- Phát triển kỹ năng DevOps và cloud computing
- Không ngừng học hỏi và cập nhật công nghệ mới
Cơ hội nghề nghiệp rộng mở:
- Mức lương cao và ổn định hơn nhiều ngành khác
- Cơ hội remote work và freelance phong phú
- Nhu cầu tuyển dụng tăng mạnh trong các lĩnh vực hot như fintech, e-commerce
- Khả năng phát triển thành architect, technical lead hoặc CTO
Lời khuyên cuối cùng:
Backend development không chỉ là viết code mà còn là nghệ thuật thiết kế hệ thống có thể scale và maintain được. Hãy tập trung vào việc hiểu sâu các nguyên lý cơ bản thay vì chạy theo công nghệ mới. Thực hành thường xuyên với các dự án thực tế, tham gia cộng đồng developer và không ngừng học hỏi.
Với sự bùng nổ của cloud computing, AI/ML integration và IoT, tương lai của backend development vô cùng tươi sáng. Đây chính là thời điểm vàng để bắt đầu hành trình trở thành một backend developer chuyên nghiệp. Hãy bắt đầu ngay hôm nay và trở thành một phần của cộng đồng backend developer đang định hình tương lai công nghệ!